Australian healthcare practices' storage of health records means mandatory obligations apply and there is a heightened risk from cyber-attack.
Regardless of whether you use electronic or hardcopy records, the code of conduct for both dental and medical practitioners requires that “medical records are held securely and are not subject to unauthorised access.”
It is imperative as you deal with some of the most sensitive information relating to patients that you understand the repercussions of opening yourself or the practice in which you work to a cyber-attack.
In 2015-16, “organisations faced numerous malicious cyber threats on a daily basis — through spear phishing emails alone, organisations are affected up to hundreds of times a day” – Australian Cyber Security Survey, April 2017”.
Threats
Malware and ransomware
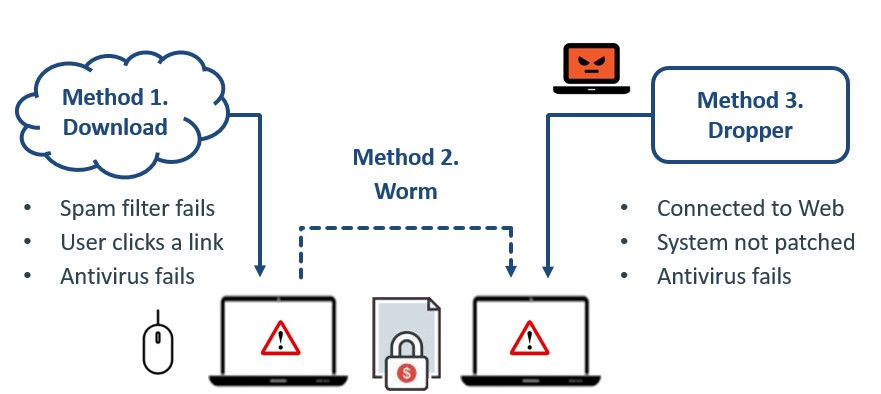
Malware is the most commonly known form of harmful software. Once malware is installed in your computer, the results can be detrimental; from taking control of your machine and encrypting files to preventing access, monitoring your online activity and keystrokes, and covertly sending confidential data from your computer or network to the attacker's base.
Malware is generally installed by a user clicking on a seemingly innocent link or when opening a downloaded file or email attachment. Once installed, malware can spread by actively looking for vulnerable computers within the same local network. Your PC or network can also be targeted and criminals will attempt to ‘drop’ the malware on your system.
A firewall and anti-virus software are your best software defences. Training staff to avoid clicking on suspicious links should also be a priority.
 Phishing
Phishing
Like the aquatically recreational activity suggests, phishing with a ‘ph’ is a way of obtaining sensitive information like usernames, passwords and credit card information. It attempts to provide the target with a compelling reason to act. Phishing tactics include getting the user to think that the attacker is someone or something else known to get you to take an action you normally wouldn’t. Since they rely on human curiosity and impulses, phishing attacks can be difficult to stop.
The email will seem legitimate and it will have some urgency to it (eg fraudulent activity has been detected on your account). The email will contain an attachment to open or a link to click. Once the malicious attachment is opened, the malware installs itself. Links clicked on will require you to log in to complete important transactions, only for you to find out the website is a trap used to capture your credentials.
Man-in-the-middle attacks
As you browse the internet, computer servers are constantly receiving information from you to provide services. Ideally, the session between a server and your computer remains private, however, you can unknowingly be subject to an attack.
Imagine you send a postcard to a friend, then while that postcard is in transit it is read by someone and they choose to scrub out and change what you have written. This how a 'man-in-the-middle' attack works. This is one way a cyber criminal may try to steal credit card data and personal information. To avoid man-in-the-middle attacks use secure connections. Check sites you visit have https and SSL, for example this is how your searches with Google are handled and you will see this in your browser:

Weak passwords and password reuse
This issue has been addressed many times over – the reuse of passwords on multiple machines and multiple accounts. Hackers rely on the fact that with users having to log in to several accounts, they often reuse the same credentials. This allows attackers to use the repeated passwords on several accounts and websites to successfully gain access.
- Avoid reusing the same password for different systems
- Don’t use the same passwords in poor security systems as you do for high security systems as hackers can then easily acquire your password
- Variety in your passwords is hard to manage but essential
- Try a password management app or website to assist with more complex passwords
- Password generator sites will assist you to generate strong passwords, eg http://passwordsgenerator.net/
Get advice to suit your circumstances
MIPS’ expertise is providing clinico-legal indemnity and assistance and other benefits of membership for health care professionals… we are not cyber security experts.
The information provided in this article is general advice, members should always seek independent expert advice based on their individual circumstances.
 Phishing
Phishing
